What is ADHD?
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a disorder that affects behavior. A recent national study reported by the CDC noted that 11% of school aged children are being diagnosed with ADHD. Three main symptoms define ADHD including inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. The symptoms are severe enough to affect the child’s behavior in social situations and at school.
Inattention Symptoms in ADHD
A child who has inattention associated with ADHD may have trouble paying attention to the task at hand. Whether related to schoolwork or play, a child with inattention may become easily bored and have trouble focusing on an activity.
Hyperactivity Symptoms in ADHD
Sitting may be intolerable for ADHD children. They may get up out of their seat at school or at other times when there is an expectation to remain seated.
Impulsivity Symptoms in ADHD 
Impulsivity Symptoms in ADHD children have trouble taking turns. They may find it difficult or unbearable to wait their turn while playing a game or doing other activities.
Other Concerns & Conditions
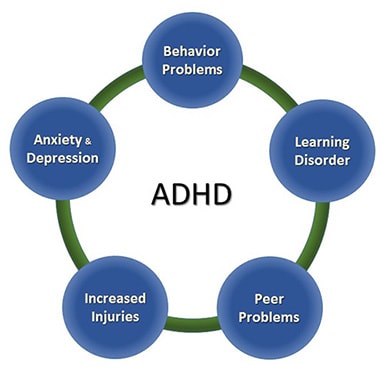
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) often occurs with other disorders. About half of children with ADHD referred to clinics have other disorders as well as ADHD.
The combination of ADHD with other disorders often presents extra challenges for children, parents, educators, and healthcare providers. Therefore, it is important for doctors to screen every child with ADHD for other disorders and problems. This page provides an overview of the more common conditions and concerns that can occur with ADHD. Talk with your doctor if you have concerns about your child’s symptoms.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends
Every child with ADHD should be screened for other disorders and problems.
Behavior or Conduct Problems
Children occasionally act angry or defiant around adults or respond aggressively when they are upset. When these behaviors persist over time, or are severe, they can become a behavior disorder. Children with ADHD are more likely to be diagnosed with a behavior disorder such as Oppositional Defiant Disorder or Conduct Disorder. About 1 in 4 children with ADHD have a diagnosed behavior disorder.
Oppositional Defiant Disorder
When children act out persistently so that it causes serious problems at home, in school, or with peers, they may be diagnosed with Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD). ODD is one of the most common disorders occurring with ADHD. ODD usually starts before 8 years of age, but can also occur in adolescents. Children with ODD may be most likely to act oppositional or defiant around people they know well, such as family members or a regular care provider. Children with ODD show these behaviors more often than other children their age.
Examples of ODD behaviors include
- Often losing their temper
- Arguing with adults or refusing to comply with adults’ rules or requests
- Often getting angry, being resentful, or wanting to hurt someone who they feel has hurt them or caused problems for them
- Deliberately annoying others; easily becoming annoyed with others
- Often blaming other people for their own mistakes or misbehavior

